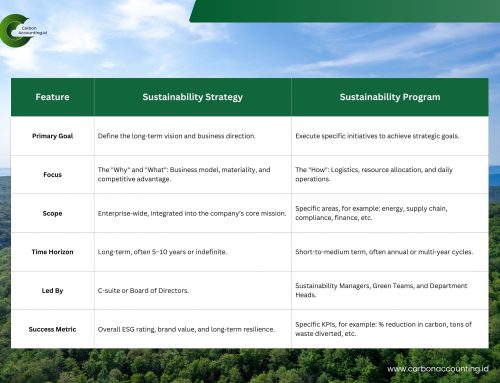
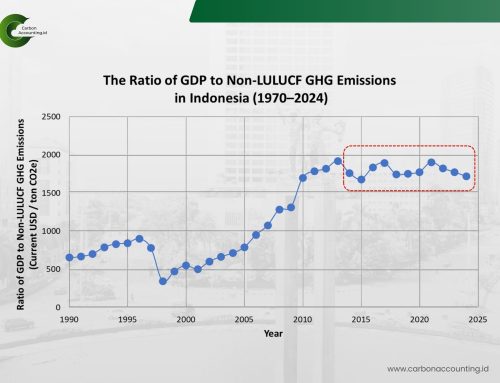
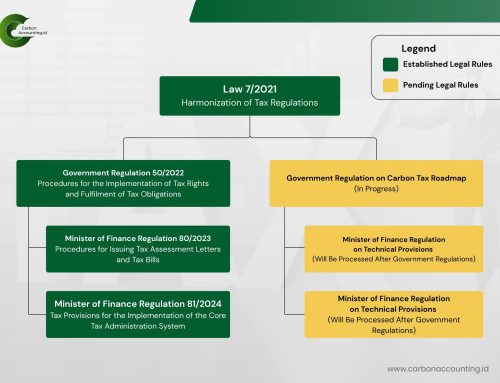
Data to Decarbonization: Ametis Supports Ngurah Rai Airport’s Net-Zero Path
The international airport ecosystem is vast and Bali’s I Gusti Ngurah Rai International Airport is a case in point. Within its perimeter operate dozens of government agencies and hundreds of commercial partners, from ground handlers and airlines to retail, logistics, and service vendors. Mapping that footprint into a single greenhouse-gas (GHG) inventory is a formidable undertaking, especially when Scope 3 emissions (those generated by tenants, suppliers, and passenger and employee travel) are counted in line with guidance from the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) and Airports Council International (ACI).
PT Angkasa Pura Indonesia has turned to the Ametis Institute’s Sustainable Economy Division to help bring order and rigor to that challenge. The assignment covers two pillars: a comprehensive GHG emissions inventory and a decarbonization roadmap tailored to the operational realities of I Gusti Ngurah Rai Airport. The objective is not only to quantify emissions accurately but to build a credible pathway that aligns with global best practices while remaining workable for Indonesia’s regulatory and institutional context.
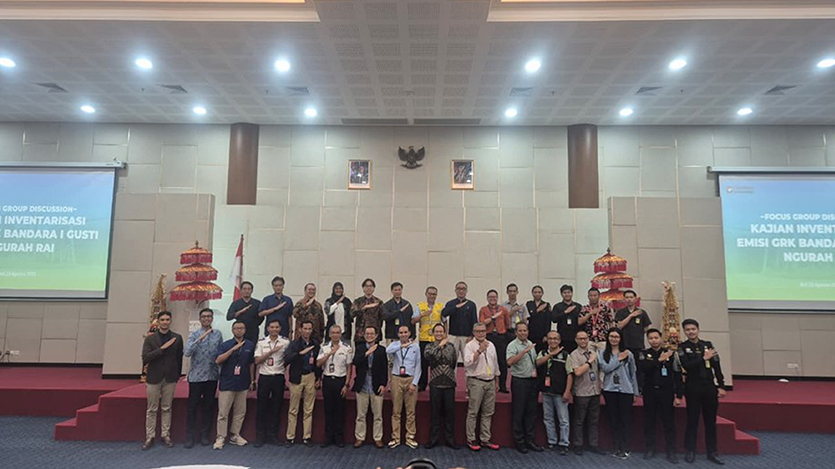
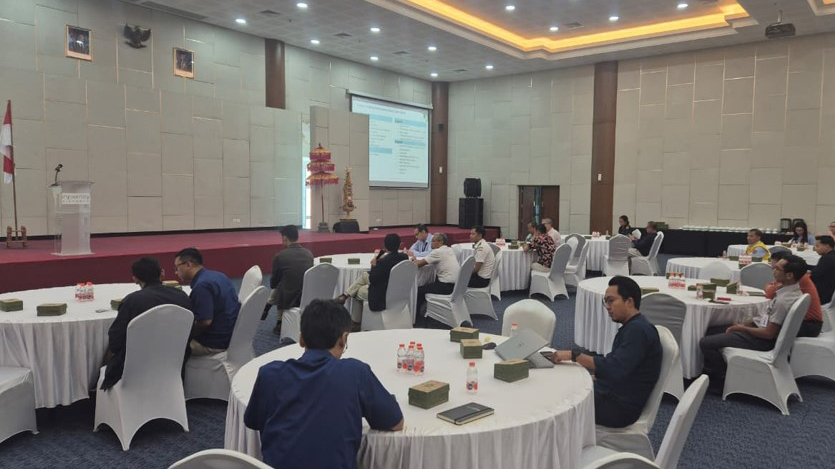
Work began with a Focus Group Discussion (FGD) on August 13, 2015, convening airport operators, government representatives, and commercial partners. The kickoff session served two purposes: outreach to ensure all parties understood the scope and stakes of the exercise, and coalition-building to secure participation in data sharing. For a facility with so many actors and interfaces, early clarity on roles, timelines, and standards is essential.
Stakeholder support is more than a procedural step, it is the backbone of data integrity. Accurate Scope 1 and Scope 2 figures depend on consistent metering and reporting by the operator, while Scope 3 requires cooperation from airlines, tenants, vendors, and service providers whose activities significantly influence the airport’s overall footprint. By aligning participants around common definitions, boundaries, and verification protocols, the project aims to produce figures that withstand scrutiny and guide investment decisions.
From this foundation, the decarbonization roadmap will prioritize actions across operations and partnerships, energy efficiency, on-site renewables, low-carbon ground access, waste and refrigerant management, and engagement mechanisms for airlines and tenants. The end goal is a living plan, one that can be implemented in phases, audited against ICAO/ACI benchmarks, and updated as technologies, policies, and traffic patterns evolve, positioning I Gusti Ngurah Rai International Airport to lead on credible, measurable climate action in Indonesia’s aviation sector.
Data to Decarbonization: Ametis Supports Ngurah Rai Airport’s Net-Zero Path
The international airport ecosystem is vast and Bali’s I Gusti Ngurah Rai International Airport is a case in point. Within its perimeter operate dozens of government agencies and hundreds of commercial partners, from ground handlers and airlines to retail, logistics, and service vendors. Mapping that footprint into a single greenhouse-gas (GHG) inventory is a formidable undertaking, especially when Scope 3 emissions (those generated by tenants, suppliers, and passenger and employee travel) are counted in line with guidance from the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) and Airports Council International (ACI).
PT Angkasa Pura Indonesia has turned to the Ametis Institute’s Sustainable Economy Division to help bring order and rigor to that challenge. The assignment covers two pillars: a comprehensive GHG emissions inventory and a decarbonization roadmap tailored to the operational realities of I Gusti Ngurah Rai Airport. The objective is not only to quantify emissions accurately but to build a credible pathway that aligns with global best practices while remaining workable for Indonesia’s regulatory and institutional context.
Work began with a Focus Group Discussion (FGD) on August 13, 2015, convening airport operators, government representatives, and commercial partners. The kickoff session served two purposes: outreach to ensure all parties understood the scope and stakes of the exercise, and coalition-building to secure participation in data sharing. For a facility with so many actors and interfaces, early clarity on roles, timelines, and standards is essential.
Stakeholder support is more than a procedural step, it is the backbone of data integrity. Accurate Scope 1 and Scope 2 figures depend on consistent metering and reporting by the operator, while Scope 3 requires cooperation from airlines, tenants, vendors, and service providers whose activities significantly influence the airport’s overall footprint. By aligning participants around common definitions, boundaries, and verification protocols, the project aims to produce figures that withstand scrutiny and guide investment decisions.
From this foundation, the decarbonization roadmap will prioritize actions across operations and partnerships, energy efficiency, on-site renewables, low-carbon ground access, waste and refrigerant management, and engagement mechanisms for airlines and tenants. The end goal is a living plan, one that can be implemented in phases, audited against ICAO/ACI benchmarks, and updated as technologies, policies, and traffic patterns evolve, positioning I Gusti Ngurah Rai International Airport to lead on credible, measurable climate action in Indonesia’s aviation sector.